A Fight To Eradicate Poverty
There is no denial of the glaring social gap between the haves and the have not’s in society.
From time immemorial, the poor have existed and as society continues to evolve and develop, their presence will be evident. Hence the need for measures to be put in place to close this gap if sustainable development is to be attained in this world.
Sustainable development is defined as development that meets the needs of the present and future generations through balancing economic, social and environmental considerations.
Every day, many people, especially in third-world countries, hardly survive the pressures of poverty which cause many to engage in unworthy activities. The extreme state of poverty has caught the attention of great leaders who see the need to resolve this issue; hence, the United Nations (UN) set out specific goals for all counties by 2030 to attain a sustainable society. The goal of eradicating poverty is one of the seventeen that the United Nations penned down. Social justice has been identified as one effective way to end poverty in our world for sustainable development.
Sustainable Development Goal 1
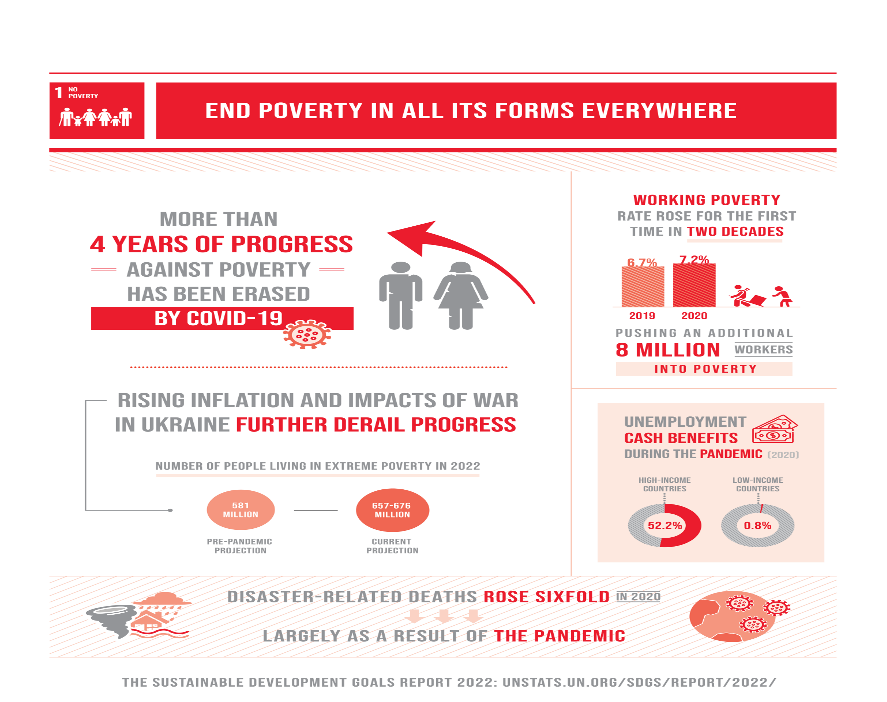
 Globally, more than 800 million people live on less than $1.25 daily; many lack fundamental amenities such as food, clean drinking water and healthy sanitation. The citizens of South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa are the most affected, as about 80 per cent of these people live in extreme poverty. Also, the proportion of women who experience living in poverty is most likely more than men as women are at a disadvantage due to unequal access to education, salary and many more.
Globally, more than 800 million people live on less than $1.25 daily; many lack fundamental amenities such as food, clean drinking water and healthy sanitation. The citizens of South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa are the most affected, as about 80 per cent of these people live in extreme poverty. Also, the proportion of women who experience living in poverty is most likely more than men as women are at a disadvantage due to unequal access to education, salary and many more.
There has been the existence of poverty for ages and various action plans have been used to aid tackle it and this has led to a reduction in the rate of poverty over the years. However, much of the progress made on poverty has been reversed and the world has graduated into a state of extreme poverty in 2020 due to the economic pressure it has been experiencing as it is still recovering from the blow it received due to the coronavirus pandemic (COVID – 19) and its aftermath.
Statistical records show that, between the years of 2015 to 2018, the percentage of poverty dropped from 10.1 per cent to 8.6 per cent; however, in 2019, there was an increase from 8.3 to 9.2 in 2020. Also, there was a reduction of workers living in poverty from 14 per cent to 6.6 per cent between 2010 to 2019.
Unfortunately, in 2020 the global progress made was affected due to the pandemic, and the percentage increased from 6.7 to 7.2 from 2019 to 2020. Furthermore, the Ukraine-Russian war has impacted the inflation rates, compounding the rate of extreme poverty being experienced as about 95 million people have been added to the people living in poverty.
The State Of Extreme Poverty In The World And The Factors Contributing To It
 Eradicating poverty is a major global challenge and a prerequisite for sustainable development. It is one of the 17 global goals of the 2030 agenda for Sustainable Development. For development to be sustainable, then it needs to be inclusive.
Eradicating poverty is a major global challenge and a prerequisite for sustainable development. It is one of the 17 global goals of the 2030 agenda for Sustainable Development. For development to be sustainable, then it needs to be inclusive.
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Goal to eradicate poverty has set action plans towards fulfilling this goal, including social justice. Social Justice is an equal society for all taking into consideration the right and development of people for the eradication of poverty, an act of justice.
The concept of social justice refers to human rights specifically focused on improving the lives of marginalized groups, be it based on ethnicity, race, nationality, gender, age, sexual orientation, religion or disability. The target is to create action plans using seven targets to eradicate poverty in all forms and levels.
These seven action plans include; eradicating extreme poverty for all people; reducing poverty by at least 50% in all categories by 2030 according to national and international; implementing social protections to achieve substantial coverage of the poor and vulnerable; equal rights to ownership, basic service, technology, and economic resource as the poor and vulnerable also have equal rights and access to all forms of resources; build resistance to environmental and economic social disasters; mobilize resources to implement policies to end poverty and creating pro-poor and gender-sensitive policy frameworks at national, regional and international levels to support accelerated investments aimed at poverty reduction.
The rule of law is an essential precondition for sustainable economic development. To achieve progress in attaining eradication of poverty, the poor must enjoy the rule of law and functioning institutions of justice; else, extreme poverty will worsen because the power would continue to be at a significant advantage while the poor continually remain at their mercy because the powerful will continue to exploit the poor. Social justice as a means to eradicate poverty hence is the application of the rule of law to aid in redistributing power to enhance the well-being of individuals through equal access to all types of amenities, be it economic, social, or physical. Therefore, an effective justice system is crucial in securing a capable and accountable state. Goal 16 of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals tackles the issue of “access to justice” and ensuring legal access to one’s rights and identity, such as birth registration.
With the backing of the law and the system of legal rights and obligations, poverty eradication is an achievable aim. The legal responsibilities of poverty eradication could be categorized into four types: the moral obligations in soft law (e.g., charitable donation), the contractual obligations in private law, the institutional obligations and mandatory obligations in public law, the interventional obligations and the relief obligations in social law.
A fundamental principle of social justice is human rights. Regardless of an individual’s status in life, one’s right cannot be taken for granted. An individual’s socioeconomic background cannot be ground to deny people their human rights and access to their entitlement. Basic rights such as freedom of speech, protection, and access to social amenities must not be denied because of poverty. Regarding all people equally in the eye of the law and justice will ease the burden of economic differences.
Another fundamental to social justice is access to resources. Given equal access to all, irrespective of socioeconomic background, with regards to education, employment, gender, status and many more is a great leap to aid eradicate poverty as financial barriers created by economic differences would be eliminated in all these areas and all would enjoy and benefit from quality access to resources.
Inclusion and participation are other vital principles in social justice. This is a stage of empowerment of all, including the grassroots, to be involved in affairs that affect them hence putting them at a level of valuing their self-worth and owning what is theirs. At this stage, the vulnerable would have a voice and can no longer be cheated.
The vision of eradicating poverty is a challenging journey. Still, it is possible if all are committed to this journey, ensuring social justice at every level, be it local, national or international.
As stated by the UN-appointed human rights expert Olivier de Schutter, although the global cost-of-living crisis happens to be a significant obstacle to eradicating poverty by 2030, countries can still make significant progress towards this Sustainable Development Goal (SDG).


